The Path to a Greener Future: Understanding Sustainable Development In an era where environmental challenges and resource depletion are becoming increasingly evident, the concept of sustainable development has gained significant importance. Sustainable development aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This blog post will explore the principles, goals, and strategies of sustainable development, highlighting its critical role in ensuring a balanced and healthy future for our planet. "Transforming our world: The path to sustainable development." What is Sustainable Development? Sustainable development is a holistic approach that integrates economic growth, environmental protection, and social equity. It seeks to create a harmonious relationship between human activities and the natural world, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and responsibly. Definition: The most widely recognized de...
Welcome Back! 😄In my last post I have taught you about Final Accounts right! 😀Well you must remember 🤔we prepare final account from trial balance and till now we only deal with closing stock as an adjustment. In this lesson I'm going to teach you how to deal with adjustment entries in final accounts.
Adjustment entries are generally given in the question after trial balance and all items given in the trial balance are recorded only once in Trading account or Profit and Loss account or Balance Sheet whereas when there are items below the trial balance then theses entries are called adjustment entries which is incomplete entries or those transactions which happened after preparing trial balance so they are not recorded in journal so we need to pass those entries in closing entries which we have learned earlier itself and post them in final accounts twice.
Second time the same entry will be recorded/adjusted in Balance sheet.
The aim of adjustments is to include in or exclude all the expenses and incomes related to the trading period in the final accounts. All adjustments are unrecorded items and they do not appear in the trial balance. So before final accounts are prepared these items should be adjusted and recorded, each in two different accounts.
2. Outstanding expenses – i) add in concerned expenses in trading A/c or P & L A/c and ii) liabilities side of balance sheet.
3. Unexpired or prepaid expenses – i) deduct from concerned expenses in trading A/c or profit and loss a/c and ii) shown in asset side of balance sheet.
4. Outstanding or accrued income – i) added in concerned income in P&L A/c and ii) shown in asset side of Balance Sheet
5. Income received in advance – i) deducted from the concern income in P&L A/c and ii) shown in liabilities side of balance sheet.
6. Depreciation – i) debit side of P&L A/c and ii) deduction from the concerned asset in Balance sheet.
7. Interest on capital – i) debit side of P&L A/c and ii) added to capital in Balance sheet.
8. Interest on Drawings – i) shown as income in credit side of P&L a/c and ii) added to drawings which is ultimately deducted from capital in balance sheet.
9. Bad debts – i) it is shown on the debit side of P&L a/c and ii) deduct form sundry debtor in balance sheet.
10. Provision for doubtful debts – i) provision for doubtful debt in trail balance is called as Old Provision and provision in adjustment is called as New Provision. In case the new provision is more than the old provision it is debited to Profit and Loss account. In case the old provision is more than the new provision than it is credited in P&L a/c and ii) in both cases new provision for doubtful debts will be deducted from debtors.
11. Provision for discount on debtors – i) debit side of P&L a/c and ii) deducted from sundry debtors on asset side of balance sheet.
12. Reserve for discount on creditors – i) credit side of P&L a/c and ii) deduct form sundry creditors in balance sheet.
13. Accidental losses – i) debited in P&L A/c and ii) deduct from particular asset in balance sheet.
a) Good insured and full claim is admitted by the insurance company – i) credit side of trading a/c and ii) asset side of the balance sheet.
b) Goods are insured and insurance company admits a part of the claim – i) credit side of trading a/c ii) amount of the claim accepted by insurance company is shown on the asset side of the balance sheet and iii) amount not accepted is a loss so debited to P&L A/c.
c) When the goods are not insured – i) credit side of trading a/c and ii) debit side of P&L a/c.
14. Goods distributed as free samples – i) deducted from purchases in trading a/c and ii) debited in P&L a/c
15. Good withdrawn for personal use – i) deducted as drawing from purchases in trading a/c and ii) deducted as drawing from capital in balance sheet.
16. Commission to manager based on net profit – i) debit side of P&L A/c and ii) liabilities side of balance sheet.
Calculation of commission:
a) If commission is payable on net profit before charging such commission:
Commission = Rate x Net profit before commission ÷ 100
b) If commission is payable on net profit after charging such commission:
Commission = Rate x Net profit before commission ÷100
17. Good received but not recorded in books – i) add in purchases in trading account and ii) add in Creditor in liabilities side of balance sheet.
18. Profit is to be carried to reserve fund – calculate net profit as usual. calculate reserve fund on net profit.iii) debit side of P&L a/c and ii) add in reserve fund in balance sheet.
19. Hidden adjustment regarding interest on loan and income from investments – some adjustment are not given in the problems, but they are implied, hence have to be made without being asked.
Example:
loan taken at 10 % as on 1-1-2013 50,000
Interest paid on loan 2,500
But interest on loan at 10% is 5000, means 2,500 is interest payable so two effects are as i) add in interest on loan debits side of P&L a/c ii) add as outstanding interest to loans liabilities side of balance sheet .
Adjustments:
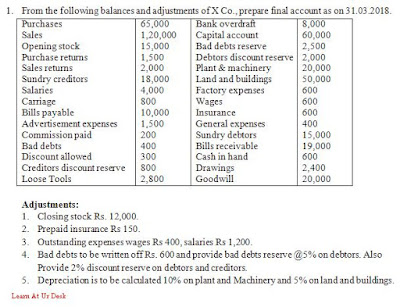
1. Closing stock Rs. 12,000. T.A(Cr) and B.S(A)
2. Prepaid insurance Rs 150. P.A(Dr) – from Insurance and B.S(A)
3. Outstanding expenses wages Rs 400, T.A(Dr) + to wages and B.S(L)
Salaries Rs 1,200. P.A (Dr) + to salaries and B.S (L)
4. Bad debts to be written off Rs. 600 and provide reserve for bad debts @5% on debtors. Also Provide 2% discount reserve on debtors and creditors.
For this adjustment I recommend 👩🏫doing working notes as Bad Debts, reserve for bad debt and discount on debtors are calculated on Sundry Debtors. And the same working note will be taken in balance sheet Asset side and another will be in profit and loss account.
Next, Provide 2% discount reserve on creditors also. It is calculated on sundry creditor’s amount
(18,000*2/100 =360) *P.A (Dr) – from discount reserve of trial balance. And B.S (L) – from creditors
5. Depreciation is to be calculated 10% on plant and Machinery (20,000*10/100 =2000) P.A(Dr)
and (20,000 – 2000 = 18000) B.S (A)
5% depreciation on land and buildings. (50,000*5/100 =2500) P.A (Dr)
and (50,000 – 2500 = 47,500) B.S (A)
now let’s dig in for solution. here I’m preparing trading account and profit and loss account combined as both are nominal account we know nominal account rules (Dr all expenses and losses and Cr all incomes and gains) .
First begin with trading account and take all T.A (Dr)/(Cr) marked items, look out for adjustment entries and then balance both sides, here in this problem we got gross profit of Rs.49,100
Next continue profit and loss Account in the same account but below the totals of Trading Account, carry forward gross profit as “By Gross Profit” and now take all P.A (Dr)/(Cr) marked items, here as well look out for adjustment entries. Before you balance both sides make sure you must cover all adjustment entries one time. First effect of an adjustment entry will be in Trading account or Profit and loss account. For your understanding I have put * as well as adj in question for pointing that entry is an adjustment entry. Here in this problem after balancing with adjustments we got Net profit of Rs 38,616.
Lastly, we prepare Balance sheet so take all B.S (L)/(A) marked items, here don’t forget👩🏫 to transfer Net profit to capital amount and the working notes which I did while explaining question. Before balancing both sides make sure you see all adjustment entries again. As the second effect of all adjustment entries will be in balance sheet, if you forget any entry your balance sheet is not going to Tally and you know the rule Balance Sheet’s both asset and liabilities are always equal. 🤷♀️Here in this problem, balance sheet tallies with 1, 33,456.
SOLUTION: Here’ how our final account with adjustment will be:
Note: make sure at this stage you see adjustment entries🔖 once before closing profit and loss account as there may be an adjustment which is not there in our markings. In short, all adjustments should cover in these accounts once☝️. Next is Balance Sheet
DO IT YOURSELF (DIY):
Adjustment entries are generally given in the question after trial balance and all items given in the trial balance are recorded only once in Trading account or Profit and Loss account or Balance Sheet whereas when there are items below the trial balance then theses entries are called adjustment entries which is incomplete entries or those transactions which happened after preparing trial balance so they are not recorded in journal so we need to pass those entries in closing entries which we have learned earlier itself and post them in final accounts twice.
Always remember 👩🏫Adjustment entries are recorded two times:
First time, entry will be recorded/adjusted in Trading Account or Profit and Loss Account andSecond time the same entry will be recorded/adjusted in Balance sheet.
ADJUSTMENTS
Adjustment is the process of adjusting outstanding and prepaid expenses and incomes, depreciation of assets, bad debt, interest on capital and drawings etc., into the final accounts.The aim of adjustments is to include in or exclude all the expenses and incomes related to the trading period in the final accounts. All adjustments are unrecorded items and they do not appear in the trial balance. So before final accounts are prepared these items should be adjusted and recorded, each in two different accounts.
The following are the usual adjustments which are to be made at the end of the accounting period:
1. Closing stock – i) trading a/c credit side and ii) asset side of balance sheet.2. Outstanding expenses – i) add in concerned expenses in trading A/c or P & L A/c and ii) liabilities side of balance sheet.
3. Unexpired or prepaid expenses – i) deduct from concerned expenses in trading A/c or profit and loss a/c and ii) shown in asset side of balance sheet.
4. Outstanding or accrued income – i) added in concerned income in P&L A/c and ii) shown in asset side of Balance Sheet
5. Income received in advance – i) deducted from the concern income in P&L A/c and ii) shown in liabilities side of balance sheet.
6. Depreciation – i) debit side of P&L A/c and ii) deduction from the concerned asset in Balance sheet.
7. Interest on capital – i) debit side of P&L A/c and ii) added to capital in Balance sheet.
8. Interest on Drawings – i) shown as income in credit side of P&L a/c and ii) added to drawings which is ultimately deducted from capital in balance sheet.
9. Bad debts – i) it is shown on the debit side of P&L a/c and ii) deduct form sundry debtor in balance sheet.
10. Provision for doubtful debts – i) provision for doubtful debt in trail balance is called as Old Provision and provision in adjustment is called as New Provision. In case the new provision is more than the old provision it is debited to Profit and Loss account. In case the old provision is more than the new provision than it is credited in P&L a/c and ii) in both cases new provision for doubtful debts will be deducted from debtors.
11. Provision for discount on debtors – i) debit side of P&L a/c and ii) deducted from sundry debtors on asset side of balance sheet.
12. Reserve for discount on creditors – i) credit side of P&L a/c and ii) deduct form sundry creditors in balance sheet.
13. Accidental losses – i) debited in P&L A/c and ii) deduct from particular asset in balance sheet.
a) Good insured and full claim is admitted by the insurance company – i) credit side of trading a/c and ii) asset side of the balance sheet.
b) Goods are insured and insurance company admits a part of the claim – i) credit side of trading a/c ii) amount of the claim accepted by insurance company is shown on the asset side of the balance sheet and iii) amount not accepted is a loss so debited to P&L A/c.
c) When the goods are not insured – i) credit side of trading a/c and ii) debit side of P&L a/c.
14. Goods distributed as free samples – i) deducted from purchases in trading a/c and ii) debited in P&L a/c
15. Good withdrawn for personal use – i) deducted as drawing from purchases in trading a/c and ii) deducted as drawing from capital in balance sheet.
16. Commission to manager based on net profit – i) debit side of P&L A/c and ii) liabilities side of balance sheet.
Calculation of commission:
a) If commission is payable on net profit before charging such commission:
Commission = Rate x Net profit before commission ÷ 100
b) If commission is payable on net profit after charging such commission:
Commission = Rate x Net profit before commission ÷100
17. Good received but not recorded in books – i) add in purchases in trading account and ii) add in Creditor in liabilities side of balance sheet.
18. Profit is to be carried to reserve fund – calculate net profit as usual. calculate reserve fund on net profit.iii) debit side of P&L a/c and ii) add in reserve fund in balance sheet.
19. Hidden adjustment regarding interest on loan and income from investments – some adjustment are not given in the problems, but they are implied, hence have to be made without being asked.
Example:
loan taken at 10 % as on 1-1-2013 50,000
Interest paid on loan 2,500
But interest on loan at 10% is 5000, means 2,500 is interest payable so two effects are as i) add in interest on loan debits side of P&L a/c ii) add as outstanding interest to loans liabilities side of balance sheet .
Now let me give you one ☝️example problem and explain you in detail.👩🏫
EXAMPLE PROBLEM:
EXPLANATION: let us first do the markings✍Adjustments:
1. Closing stock Rs. 12,000. T.A(Cr) and B.S(A)
2. Prepaid insurance Rs 150. P.A(Dr) – from Insurance and B.S(A)
3. Outstanding expenses wages Rs 400, T.A(Dr) + to wages and B.S(L)
Salaries Rs 1,200. P.A (Dr) + to salaries and B.S (L)
4. Bad debts to be written off Rs. 600 and provide reserve for bad debts @5% on debtors. Also Provide 2% discount reserve on debtors and creditors.
For this adjustment I recommend 👩🏫doing working notes as Bad Debts, reserve for bad debt and discount on debtors are calculated on Sundry Debtors. And the same working note will be taken in balance sheet Asset side and another will be in profit and loss account.
Next, Provide 2% discount reserve on creditors also. It is calculated on sundry creditor’s amount
(18,000*2/100 =360) *P.A (Dr) – from discount reserve of trial balance. And B.S (L) – from creditors
5. Depreciation is to be calculated 10% on plant and Machinery (20,000*10/100 =2000) P.A(Dr)
and (20,000 – 2000 = 18000) B.S (A)
5% depreciation on land and buildings. (50,000*5/100 =2500) P.A (Dr)
and (50,000 – 2500 = 47,500) B.S (A)
now let’s dig in for solution. here I’m preparing trading account and profit and loss account combined as both are nominal account we know nominal account rules (Dr all expenses and losses and Cr all incomes and gains) .
First begin with trading account and take all T.A (Dr)/(Cr) marked items, look out for adjustment entries and then balance both sides, here in this problem we got gross profit of Rs.49,100
Next continue profit and loss Account in the same account but below the totals of Trading Account, carry forward gross profit as “By Gross Profit” and now take all P.A (Dr)/(Cr) marked items, here as well look out for adjustment entries. Before you balance both sides make sure you must cover all adjustment entries one time. First effect of an adjustment entry will be in Trading account or Profit and loss account. For your understanding I have put * as well as adj in question for pointing that entry is an adjustment entry. Here in this problem after balancing with adjustments we got Net profit of Rs 38,616.
Lastly, we prepare Balance sheet so take all B.S (L)/(A) marked items, here don’t forget👩🏫 to transfer Net profit to capital amount and the working notes which I did while explaining question. Before balancing both sides make sure you see all adjustment entries again. As the second effect of all adjustment entries will be in balance sheet, if you forget any entry your balance sheet is not going to Tally and you know the rule Balance Sheet’s both asset and liabilities are always equal. 🤷♀️Here in this problem, balance sheet tallies with 1, 33,456.
SOLUTION: Here’ how our final account with adjustment will be:
Note: make sure at this stage you see adjustment entries🔖 once before closing profit and loss account as there may be an adjustment which is not there in our markings. In short, all adjustments should cover in these accounts once☝️. Next is Balance Sheet
Note: before you tally both sides again just take a look 👩🏫at adjustment entries. As the second effect ✌of all adjustments have to be in balance sheet.
I hope you have learned 👩🏫how we make adjustments in final account. Now let me give you one ☝️(DIY) for your practice ✍let’s see how you will do! 🤗Well I have shared my knowledge with you let’s see did you gained that knowledge?🤷♀️
DO IT YOURSELF (DIY):






Can sales return or purchase return be in adjustment. If so, then what would be the double entry for that.
ReplyDeleteIn case of purchase return....
ReplyDeleteThe entry will be
To purchases X
less: purchase return x
--------
***
And same in case of sales return too
Asak mam i want to talk to u bcz its v urgent for my finals...my finals is approaching mam...I'm 2nd yr student...pls helpme mam...
ReplyDeleteThe imp IQ list which u gave us mam...is it help for ibe ts exams for 2021
ReplyDeleteWonderful post thank you for sharing valuable material with us.
ReplyDeleteSearching for Outsourcing of bookkeeping service .
Well-written blog. I appreciate your effort in highlighting such valuable material. This will for sure going to be helpful. Thank you for sharing.
ReplyDeletefinance and accounting outsourcing
outsourced accounting
bookkeeping outsourcing
Your blog provides well-written and informative content on a variety of accounting topics. I appreciate your efforts to share your knowledge and expertise with others.
ReplyDeleteimportance of accounting ethics
audit and accounts service ensure your financial statements are accurate and meet regulatory compliance standards. Professional auditors provide insights that help businesses improve transparency and decision-making.
ReplyDelete